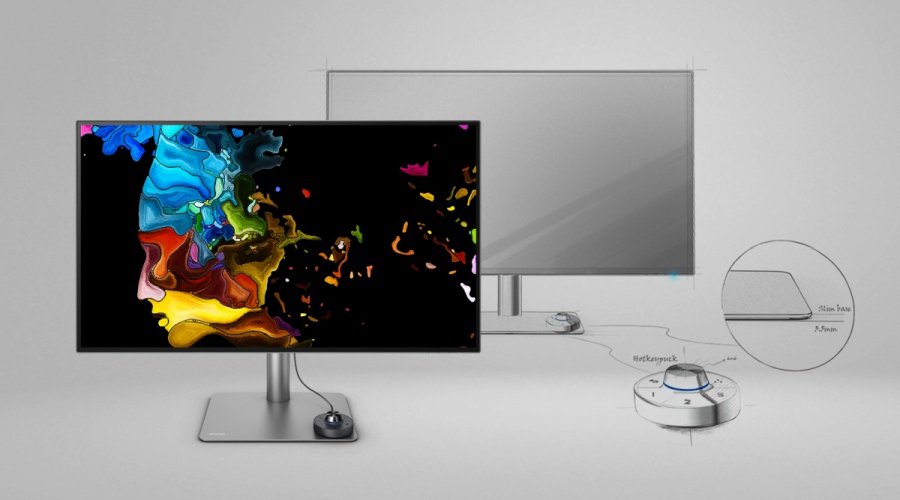
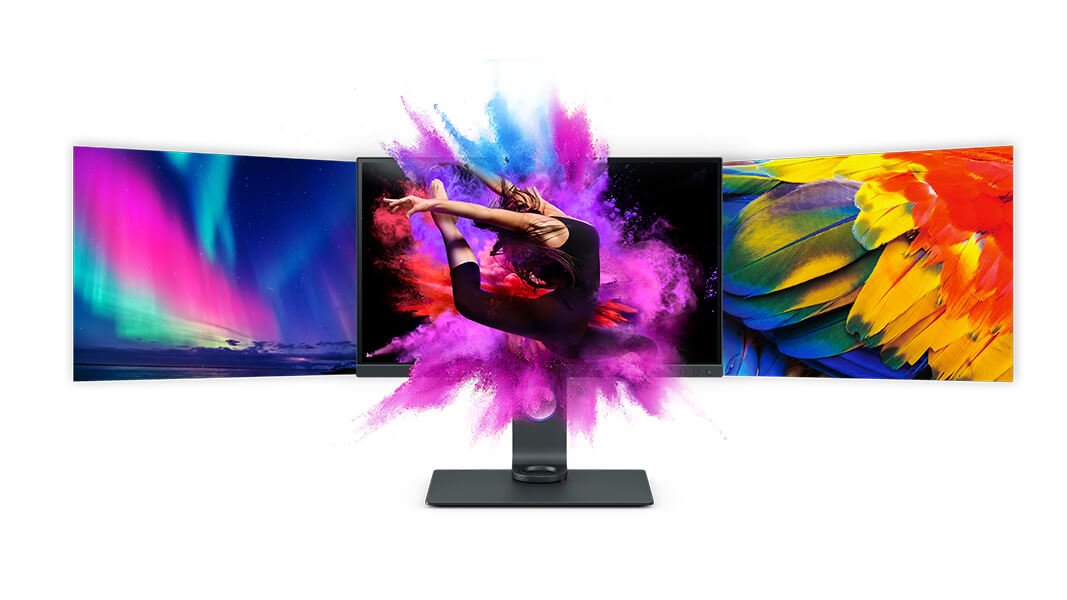
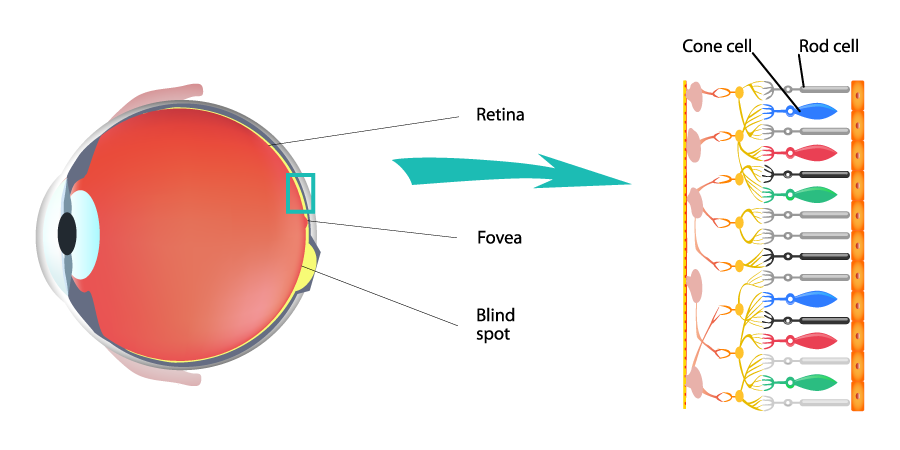
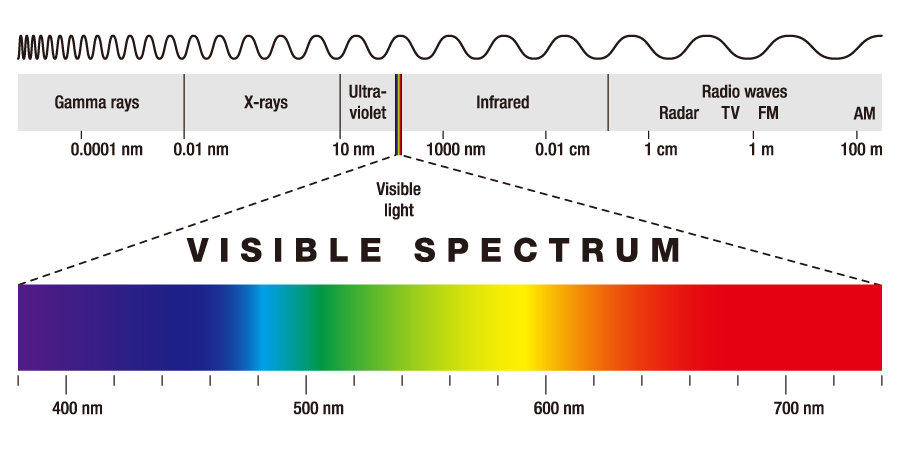
What is color? There are two types of cells in the retina of our eye that are responsible for our perception of color: rod and cone. Cones, which are sensitive to color, function best in bright light. They exist in three forms, each differing in the wavelength of light absorbed ( LMS ). Rods, on the other hand, are sensitive to the intensity of light. In the human eye, rod cells allow us to distinguish and detect objects in the dark; however, since their sensitivity to light is better than cone cells, our ability to perceive the color of objects in an area of low light becomes poor.







![How to Choose the Best Monitor for Mac® Devices [2024]](https://image.benq.com/is/image/benqco/mac-monitor_thumb?$ResponsivePreset$)

